Lutra
| Lutra | |
|---|---|

| |
| Eurasian otter (Lutra lutra) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Mustelidae |
| Subfamily: | Lutrinae |
| Genus: | Lutra Brisson, 1762 |
| Type species | |
| Mustela lutra Linnaeus, 1758
| |
| Species | |
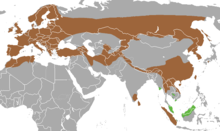
| |
| Range of Lutra lutra (brown), Lutra sumatrana (green) | |
Lutra is a genus of otters, one of seven in the subfamily Lutrinae.
Taxonomy and evolution
[edit]The genus includes these species:
Extant species
[edit]| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eurasian otter | Lutra lutra (Linnaeus, 1758) |
coasts of Europe, many parts of Asia, and parts of northern Africa
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
NT
|
| Hairy-nosed otter | Lutra sumatrana (Gray, 1865) |
Southeast Asia
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
EN
|
Extinct species
[edit]| Image | Scientific name | Common name | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
L. nippon | Japanese otter | Japan |
- †Lutra affinis
- †Lutra bressana
- †Lutra bravardi
- †Lutra castiglionis
- †Lutra euxena
- †Lutra fatimazohrae
- †Lutra franconica
- †Lutra hearsti
- †Lutra palaeindica
- †Lutra simplicidens
- †Lutra trinacriae
The genus most likely evolved in Asia during the late Pliocene epoch;[1] the oldest fossil belonging to the genus is of the species L. palaeindica, and dates from the late Pliocene.[2]
Habitat
[edit]Lutra species are semiaquatic mammals, so they are well-adapted to both water and land. They prefer shallow, narrow areas of streams surrounded by mature trees and with rocks, especially where weirs reduce the flow of the water, as well as attract fishes. They seem to tolerate roads and residential and agricultural areas, but only moderate human interaction. They clearly avoid areas without vegetation cover and rocks.[3]
Diet
[edit]The otters' diets consist mainly of fish (hence, the aquatic environment). However, during the winter and in colder environments, fish consumption is significantly lower and the otters use other resources for their food supply. Their diets can consist of amphibians (mainly frogs and pond turtles), bird predation (mainly anserine species), small rodents, and invertebrates such as water beetles, snails, and crayfish. They have also feed on plants, specifically grasses. With this large diversity of prey and resources for their diets, otters are considered "opportunistic eaters".[4]
Behavior
[edit]Some otters live in solitude, while others live in groups.
References
[edit]- ^ Koepfli, K.-P.; et al. (2008). "Multigene phylogeny of the Mustelidae: Resolving relationships, tempo and biogeographic history of a mammalian adaptive radiation". BMC Biology. 6 (10): 10. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-6-10. PMC 2276185. PMID 18275614.
- ^ Larivière, S. (2002). "Lutra maculicollis". Mammalian Species. 712: Number 712: pp. 1–6. doi:10.1644/1545-1410(2002)712<0001:LM>2.0.CO;2. S2CID 198968980.
- ^ Cho, Hee-Sun; Choi, Kwang-Hee; Lee, Sang-Don; Park, Young-Seuk (2009). "Characterizing habitat preference of Eurasian river otter (Lutra lutra) in streams using a self-organizing map". Limnology. 10 (3): 203. Bibcode:2009Limno..10..203C. doi:10.1007/s10201-009-0275-7. S2CID 20000248.
- ^ Lanszki, József; Molnár, M. & Molnár, T. (2006). "Factors affecting the predation of otter (Lutra lutra) on European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis)". Journal of Zoology. 270 (2): 219. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2006.00132.x.









